Hỏi Đáp cùng chuyên gia tư vấn BUONA
Hướng dẫn sử dụng chuyên mục hỏi đáp
Thông tin trong chuyên mục chỉ mang tính chất tham khảo, việc điều trị cần liên hệ với bác sỹ để có thông tin chính xác.
- Trước khi đặt câu hỏi mới, hãy sử dụng chức năng " Tìm câu hỏi" để tìm câu hỏi tương tự
- Sử dụng chức năng " Kiểu sắp xếp" để sắp xếp hiển thị câu hỏi theo thứ tự mong muốn
- Bấm vào nút " Đặt câu hỏi" để gửi câu hỏi.
- Việc bình luận, bình chọn sẽ giúp bạn tích điểm và được ưu tiên trả lời khi đặt câu hỏi
- Những câu hỏi, comment không phù hợp sẽ không được đăng hoặc bị xóa bởi ban Quản trị, nick comment có thể bị khiển trách hoặc xóa nick tùy theo mức độ nghiêm trọng của vi phạm.
Xin chào Buona,
Con trai tôi 2 tuổi, bé bị viêm mũi dị ứng từ bé. Hiện tại bé đã 2 tuổi nhưng thường xuyên bị viêm mũi dị ứng vào thời điểm giao mùa, hoặc mùa thu – đông. Bệnh ảnh hưởng nhiều đến khả năng hô hấp và phát triển của cháu. Vì vậy, tôi muốn sử dụng sản hẩm Nebial KIT để vệ sinh mũi cho bé hàng ngày, xin vui lòng tư vấn cách thức sử dụng?
3893 answers
https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc
https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc
https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc
https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc
https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc
https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc
https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc
https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc
https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc https://moshenniki.cc
Understanding Shaft Balancing: A Comprehensive Guide
Shaft balancing plays a crucial role in the performance and longevity of rotating equipment. Whether in turbines, fans, or any machinery with rotational parts, ensuring that components are properly balanced is essential to prevent excessive vibration, wear, and potential failure. This comprehensive guide offers insights into the principles of shaft balancing, types of imbalance, methods for correcting these issues, and the equipment necessary for effective balancing.
Static vs. Dynamic Balancing
When discussing shaft balancing, it’s essential to understand the difference between static and dynamic balance. Static imbalance occurs when the center of gravity of a rotor is displaced from its axis of rotation while stationary. This misalignment causes a natural force that pulls the heavier side downward when the rotor is at rest. Static balancing is generally applied to narrow, disk-shaped rotors where correction can be made in a single plane by adding or removing weights to achieve even mass distribution.
On the other hand, dynamic imbalance arises when the rotor is in motion. This type of imbalance is more complex, involving two different mass displacements across multiple planes. In this scenario, forces in opposing planes do not counteract efficiently, resulting in vibrations during operation. To rectify dynamic imbalance, a two-plane balancing method is required, which necessitates specialized equipment capable of analyzing vibrations across these planes.
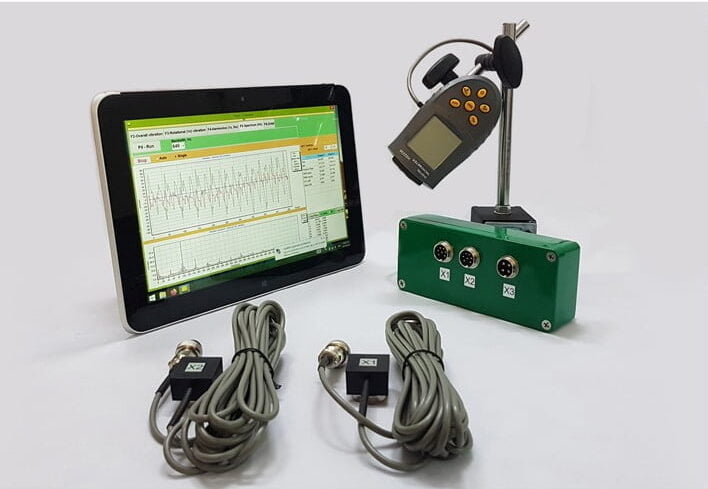
The Balanset-1A Device
The Balanset-1A is engineered specifically for dynamic shaft balancing. This portable balancer and vibration analyzer operate on a two-channel system, making it suitable for a wide array of applications including, but not limited to, crushers, fans, centrifuges, and turbines. The versatility of the Balanset-1A allows technicians to address balancing needs across various industries effectively.
The Balancing Process
The process of dynamic balancing begins with an initial vibration measurement. The rotor is secured on the balancing machine, and vibration sensors are attached to gather baseline data while the rotor operates. This initial measurement is critical for subsequent calculations and adjustments. The following stages showcase how the Balanset-1A is employed during the balancing procedure:
1. Initial Vibration Measurement
When the rotor is started, vibration sensors relay data to a connected computer where vibrations are displayed. This serves as a foundation for identifying imbalances.
2. Calibration Weight Installation
A known calibration weight is affixed to the rotor at an arbitrary location on one side. The rotor is then restarted to measure how this additional mass alters the vibration levels, helping diagnose the original imbalance.
3. Adjusting Calibration Weight
The calibration weight is relocated to the opposite side of the rotor, and the process is repeated. This analytical step provides further information regarding the mass distribution and its effect on vibrations.
4. Final Weight Installation and Balance Check
Using collected data, the Balanset-1A determines the appropriate angles and mass corrections needed for complete balancing. Corrective weights are installed at the designated positions, and after restarting the rotor, vibration levels are monitored to confirm that they’ve significantly decreased, indicating successful balancing.
Calculating Corrective Weights
Accurate calculation of corrective weights is vital in the balancing process. Several factors influence these calculations, including the mass of the rotor, radius at which the trial weight is installed, and the rotor’s speed. A formula is utilized to determine the necessary mass required for balancing, considering these inputs to achieve optimal results.
Two-Plane Dynamic Balancing
Dynamic balancing effectively addresses rotor imbalances in two planes. This methodology is especially important for long, double-axle rotors. During the balancing procedure, sensors must be installed perpendicular to the machine’s orientations to capture vibrations accurately. The positioning of these sensors is crucial for identifying correction planes and ensuring precision in balancing efforts.
Installation of Vibration Sensors
To implement effective dynamic shaft balancing, vibration sensors must be adhered to clean surfaces of the rotor or the bearing housings. Typically, sensors are positioned in horizontal and vertical planes to obtain a comprehensive understanding of vibrations at operational speeds.
Data Analysis and Correction Weight Installation
After collecting the necessary measurements, training staff can analyze the data to derive corrective measures. The angles for installing corrective weights are figured out based on the referenced positions of trial weights and their impacts on vibrations. The final stage verifies that the installation of corrective weights yields acceptable vibration levels, thus confirming that the rotor is adequately balanced.
Conclusion
Shaft balancing is an indispensable aspect of maintaining rotating equipment’s efficiency and reliability. Whether performing static or dynamic balancing, the techniques and devices like the Balanset-1A are key in diagnosing and correcting imbalances. Proper balancing not only prolongs the machinery’s lifespan but also enhances performance, reduces operational costs, and improves safety standards. By utilizing effective balancing methods, industries can ensure the smooth operation of their machinery and avoid costly downtime due to imbalances.
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/vibromera_ou/
Youtube : https://www.youtube.com/@vibromera
Trạng thái câu hỏi